For decades, the western United States was ground zero for one of the greatest experiments humans had ever undertaken: replumbing the world’s rivers. As Marc Reisner cataloged so forcefully in the book Cadillac Desert, dam builders pursued these mega-projects with little regard for whether they were needed, or what effects they would have on people or the environment. It was an experiment fueled less by need than by greed.

Dam-builders undertook this gargantuan effort without clearly understanding what they would lose – the healthy, productive rivers that were once said to be so thick with fish that you could walk across a river on their bodies.
The U.S. didn’t keep this ecosystem-devastating technology to themselves. Throughout the 20th century, the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation busily exported dam technology to other countries around the world, selling these large dams as temples to modernity. Developing countries conveniently gave American companies and engineers fat contracts to build them.
Many U.S. dams are now nearing the end of their lifespan, and dam removals have increased exponentially. But the hydropower boom is still reverberating through the rest of the world. Large dams are being planned and developed on major rivers like the Mekong, the Amazon, and the Congo, where millions depend directly on their rivers for food and livelihoods.
This is madness. In too many cases, local communities shoulder the financial burdens and social and environmental impacts while the developers walk away with a profit. And in an era of climate change, hydropower is a risky and insecure energy source that’s deeply vulnerable to increasingly severe droughts and floods. Furthermore, dams lower the climate resilience of riverine communities. It’s time to find another way.
Learn More
Latest News
- Thailand’s National Human Rights Commission Raises Serious Concerns about Impacts of Mekong River DamsBy Rin Sohsai In early October, the National Human Rights Commission of Thailand (NHRC) sent a letter to Thailand’s Prime Minister expressing serious concerns about the plans for four more … Read more
- MAP: Hydropower Dams in Sub-Saharan Africa
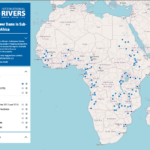 French below/ Version Française plus bas Only one-third of rivers remain free-flowing, largely due to dams. Globally, large hydropower dams have displaced up to 80 million people and compromised the … Read more
French below/ Version Française plus bas Only one-third of rivers remain free-flowing, largely due to dams. Globally, large hydropower dams have displaced up to 80 million people and compromised the … Read more - Developing news: Controversial Pak Beng Dam on the Mekong hits major milestone, despite warnings of widespread damage to environment and peopleOn September 13, the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand, or EGAT, signed a Power Purchase Agreement for the controversial Pak Beng Dam on the main stem of the Mekong River. … Read more

